According to the Office of National Statistics, for the first time in 30 years, UK households have collectively spent more than they have earned in 2017. Their total expenditure for the period came to on average £900 more than their income; thus pushing them into a financial deficit for the first time since the credit card boom of the 1980s. The deficit, which amounted to nearly £25bn, was equivalent to almost a quarter of the NHS budget. Though most households fell into the cycle of overspending with the money they had borrowed, a number of the households also ran down their savings.
The government, in its autumn budget, announced new measures to help citizens in debt. Referred to as the ‘Breathing space’ scheme and the ‘No-interest loans’ scheme, these measures aim to tackle the problem faced by about three million people in Britain, who are facing the pressure of debt caused by borrowing from high-cost lenders such as payday and credit card companies.
Currently, over 16.8 million people in Britain have less than £100 savings. This leads to financial stress and takes a toll on their mental health. Over a million people turned to high-cost credit last year to meet their basic living expenses, which is in the end counterproductive both for households and the country’s economy. The problem of high-cost credit is intensified by insecurity in the labour market and the growing use of zero-hour contracts. This, in turn, implies that when people do not plan their budget and overspend, they get into debt, as they have no savings. This will have a negative impact on their credit ratings, distancing them even further from fair credit opportunities.
Therefore, the UK government, working with leading debt charities and the banking industry, has decided to launch a feasibility study to help design a pilot for a ‘No-interest loans’ scheme in early 2019. While, under the other ‘Breathing Space’ scheme, people who are in debt will get a 60-day period of protection against creditor action. This will give them more time to seek advice and make plans to repay their debt in a manageable way.
The decision makers drew inspiration from the No Interest Loans Scheme of Australia, which provides people with low incomes access to safe, fair and affordable access to credit. The scheme offers loans of up to $1,500 for essential goods and services and not for cash. Repayments are structured over 12 – 18 months. There are no interest charges or fees.
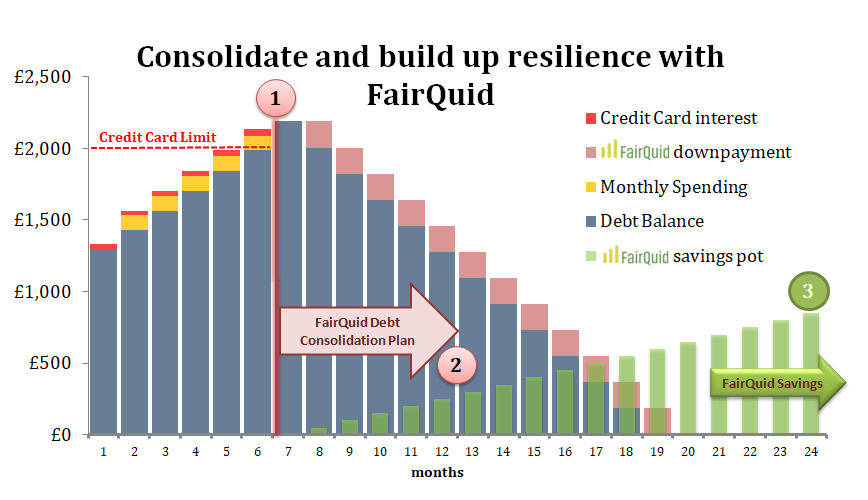
Though there are many organisations imparting financial education to create awareness for lowering debt and increase savings, there is a need for a strong practical solution that can work alongside these plans. FairQuid, a financial wellbeing platform, believes credit unions play a central role in tackling these issues.
Currently, credit unions in the United Kingdom could help millions of Britons who are excluded from mainstream finance. They play an important role in facilitating savings and offering affordable loans to their members. The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) regulates credit unions but as they are run for the benefit of members, not shareholders, they can offer ethical saving schemes, competitive loans and other financial products, not usually available to individuals excluded from traditional financial organisations.
The FairQuid Wellbeing Platform has been designed to work in tandem with employers to develop innovative solutions that benefit both credit unions and employees. It is a win-win situation for all. The platform educates employees about personalised financial tools to make better finance-related decisions and take control of their finances. On the other hand, for employers, it prevents mental health issues in workplace, boosts engagement levels, and increases employee retention.
The budget also has a provision to support this credit union sector. To help people increase their financial resilience while boosting awareness and membership of these community organisations, the budget commits to launch a pilot of a new ‘prize-linked saving’ scheme for credit unions.
By helping households manage their unexpected costs through increased access to fair and affordable credit, and motivating them to create a safety net of savings, the government is taking a big step towards its citizens “being and feeling financially secure, today and in the long run.”